
3D Printer Grades: Which One is the Best Options for You?
If you want to experience the freedom and speed that additive manufacturing can offer to your business or just want to get into 3D printing as just a hobby, you might be baffled at first because of the amount of different 3D printer models on the market.
There are hundreds of brands out there manufacturing countless 3D models, each with their own prices, features, capabilities, and purposes. Like any other electronic device, it is best to do some research before making a big investment in something that you are going to use for a long time. If you get into additive manufacturing without having an idea of what these features and capabilities are, you might regret some of the decisions you have made.
In this blog, we will talk about different segments or grades of 3D printers rather than getting into specific models and brands. They offer different advantages and come with their own shortcomings. We will mostly be talking about FDM printers as other technologies like SLA are not easy to compare with FDM machines of different segments.
3D Printer Grades
There is no clear-cut feature that divides different segments of 3D printers. The category different 3D printers fall under will be based on a rough estimation of the device’s capabilities and size.
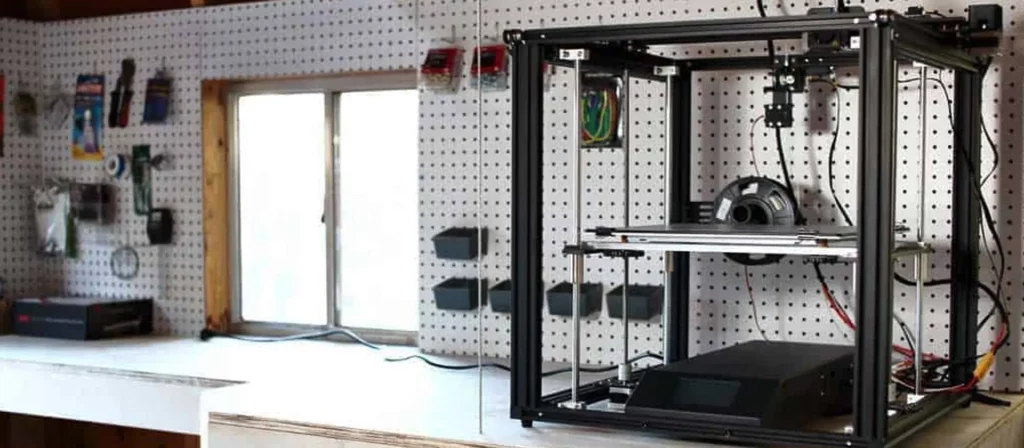

Desktop 3D Printers
Desktop 3D printers will be the segment that you come across the most often. A good chunk of the 3D printers you see on the market will fall under this category. They will be defined by their smaller build volumes and fairly affordable prices.
Desktop 3D printers are usually considered to be best-suitable for hobbyists, but there are amazing desktop 3D printers on the market that can give great results when it comes to printing speed, quality, and compatibility.

Volume
A small build volume will be the biggest shortcoming of a desktop 3D printer for most people that are looking for a 3D printer. The X-axis of a desktop printer can be as small as 120 mm and as big as 180 mm. The Z-axis will be comparable.
The size will change depending on the 3D printer of course, but the desktop segment of printers is usually not the best fit for mass production but can be used for prototyping and DIY home prints.

Quality
Don’t get us wrong, there are desktop 3D printers on the market that will give you very precise prints for very reasonable prices. But as far as quality goes, you will likely not get the same quality from an average desktop 3D printer that you would with a professional or industrial device.
Most desktop printers have open systems, which also means the consistency of the performance you get from these devices will be lower than the standard professional printer. To keep it simple, a high-end desktop 3D printer will be good enough and the cheaper ones will likely be substandard.

Materials
Desktop 3D printers usually don’t have enclosures that keep the temperatures in the print area stable, which means you won’t be able to use some filaments as consistently as you would with professional 3D printers. This is another limitation that most desktop printers will have.
If your 3D printing needs are sufficiently met with a material like PLA, they will be completely fine. But if you need to print with, let’s say ABS, you will get much better results with a printer that has an enclosure.

Professional 3D Printers
Your standard professional 3D printer will be usually much bigger, a little bit more expensive, and more versatile than the printers we described in the desktop segment. The reason most people describe these devices as “professional” is that they are usually considered to be too big for home use and they provide a level of performance that is sought after by professional businesses.
These models can go beyond hobby use and can print amazing spare parts that are meant for heavy-duty use. They will, of course, be more expensive than the average desktop 3D printer, but you will be able to get much better results with these machines.
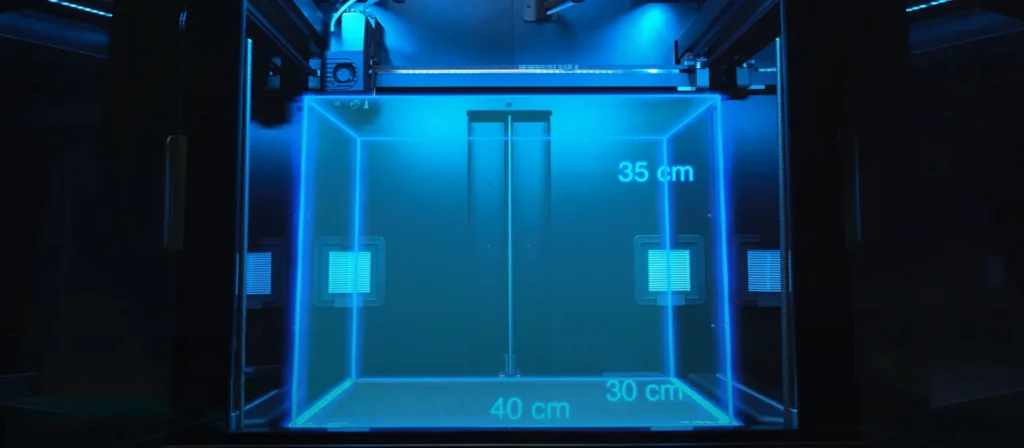
Volume
One of the defining features of professional 3D printers is their superior printing area. A bigger print volume is one of the most important things that people look for in a 3D printer. While a build volume of 180 x 180 x 180 mm will be enough for most hobbyists, the same can’t be said about businesses.
Businesses often use 3D printers for mass production and the superior size of these printers allows the users to make more than one of the same product. In most cases, the bigger the printing area the better. There is no industry standard when it comes to the build volume for professional printers, but they can easily be as big as 400 x 300 x 350 mm.

Quality
The average professional-grade 3D printer will also have a higher resolution than a desktop printer. While a low-end desktop printer can barely give you consistent results in 50 microns, most professional-grade 3D printers can guarantee you amazing quality even in 25 microns. You will be able to print objects with higher details and a better fit and tolerances with these devices.
With the addition of an enclosure, you will also be able to get more consistent results, especially with materials that need certain conditions to give good results. You will no doubt experience less warping and other unwanted troubles.

Materials
You will have a much wider array of filaments that you can choose from when you are working with a professional-grade machine. ABS, PLA, PETG, ASA, or PC-ABS are all very comfortable to print with for these 3D printers.
Also, most professional 3D printers come with the benefits of an enclosed print area. This will allow the users to print with certain materials that require exact temperatures to give good results like ABS and ASA.
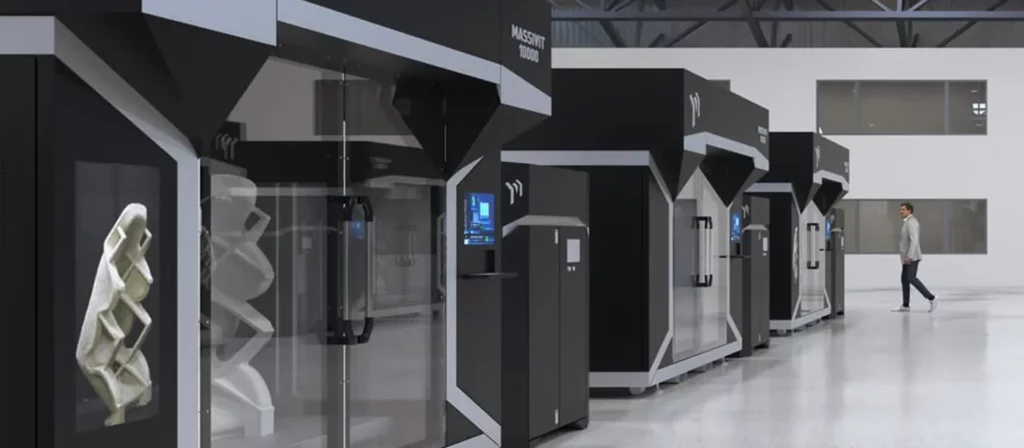

Massivit 10000 Industrial 3D Printers
Industrial 3D Printers
Industrial 3D printers don’t have the power they had in the industry due to the rapid improvements that have been made in professional-grade 3D printers. But they still have a unique place in different verticals thanks to some very advanced features they have.
Unlike the switch from a desktop printer to a professional 3D printer, the jump in the price of these segments will be colossal. While a high-end desktop costs around $1000 and a professional grade 3D printer of the same caliber will cost around 4000-7000$, a high-end industrial 3D printer can set you back $100,000 in some cases. These are not consumer-level products. Most industrial 3D printers are an investment that only some companies can make and their unique features are only necessary for certain businesses.
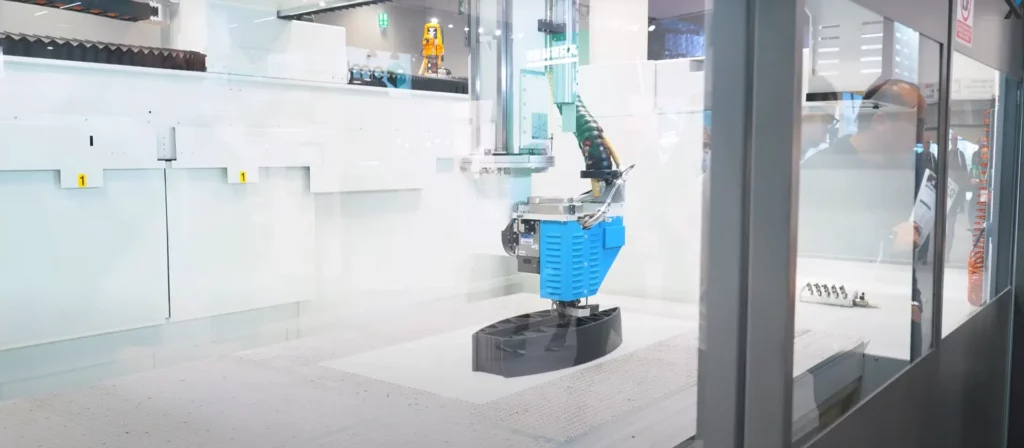

Volume
Industrial 3D printers are not limited to a certain build volume to be considered industrial grade. There are industrial 3D printers on the market with a build volume of 300 x 300 x 400 mm but there is pretty much no upper limit to how big they can get.
You can find printers that have a print volume as big as 1500 × 1200 × 1200 mm, but this is in no way the industry standard. Volumes of this size are only required for single-piece end-use parts that are to big to be printed on a professional 3D printer.
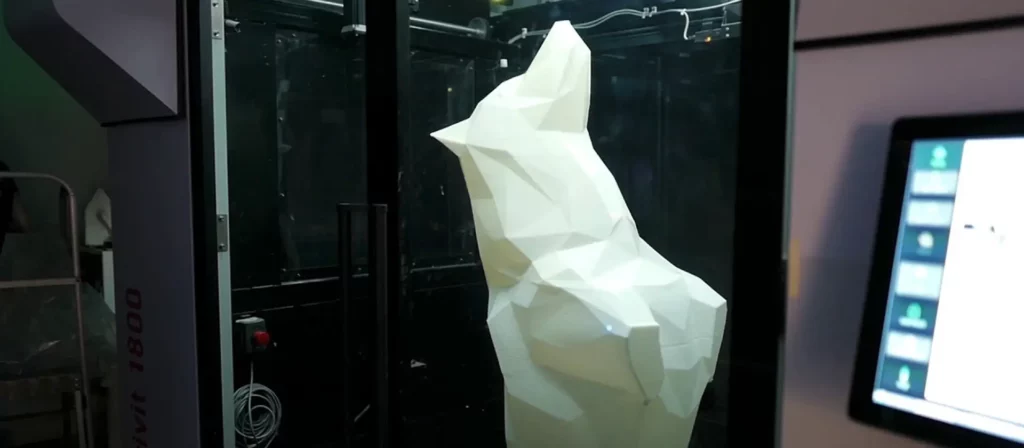

Quality
This is where these devices shine. The average industrial 3D printer has a margin of error of 0.1%. Dimensional accuracy aside, there is almost no risk of cracking and warping in these machines which makes them perfect for businesses who want to use additive manufacturing to make geometrically complex parts.
The reason these 3D printers can achieve such good results are the advanced features they have. First of all, most industrial printers will have a heated chamber that keeps the temperatures in the print area extremely precise, which eliminates warping almost completely. Secondly, these machines are equipped with top-of-the-line print heads that can give reliable results in 10-micron resolutions.
Materials
An industrial 3D printer can also achieve world-class accuracy and quality with pretty much every single filament you can find on the market. They are not limited to certain materials like a desktop 3D printer would be. ABS, PLA, and PETG are child play for these devices.
Not only that, but industrial filaments also have their own high-quality filaments that can’t be printed with desktop devices. Filaments like PEI, PEEK, PEKK, PA-CF, and PA-GF are extremely useful in some industries and can be printed with ease using industrial 3D printers.
To explore what filaments you can use with an industrial 3D printer: A Guide to Industrial Filaments
Which 3D Printer Should You Buy?
The most important factor when making a decision on which segment of 3D printing you are going to buy is your specific needs. If you just want to make little action figures and some DIY tools for home use, you won’t need anything other than a standard desktop device.
If you have a business that can benefit from rapid prototyping, mass production of highly functional 3D printed parts, or bigger than average models that couldn’t be glued together, then professional 3D printers would be the best choice for you.
And finally, industrial 3D printers will be the best fit for certain industries that can’t afford any margin of error on their printed parts and need to print their models using industrial filaments.
With the information we have provided, you can evaluate your situation and make an educated choice on which 3D printer to buy. Depending on your budget and needs, you can buy a 3D printer from any of these segments we listed above and get sufficient results. The challenge for you will be finding the sweet spot.
