
Is 3D Printing Environmentally Friendly?
The carbon footprint of humans and the effects that our actions have on the earth are becoming hot-button topics with recent discoveries that are made in the field of climate science.
People are becoming more mindful of their consumption habits to reduce the waste they create and while that is a good cause, a good chunk of the carbon emission humans produce is actually the result of incautious production methods.
Additive manufacturing has the potential to change that as a more agile production method that can adapt not only to the needs of the producers but also to the changing landscape of environmentally friendly business practices.

Sustainability in Manufacturing
We as people like to believe big changes start at a personal level and small steps taken and changes made by individuals can have a big effect, but that might not be the case. While the way individuals live has a negative effect on the environment, the majority of the carbon footprint we create is made by big manufacturing companies that are producing the goods we like.
Whether out of negligence or to cut costs, a lot of industries use non-biodegradable materials and waste countless tons of material in goods they produce as surplus.
No matter how many paper straws you use or plastic bags you decline at the grocery store, the big change would have to start at a corporate level to make actual, noticeable improvements to the environment.
Is 3D Printing Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly?
Traditional manufacturing methods have long, complicated supply chains. Each chemical you use, model you mold, and material you buy will have an ambiguous history that is hard to track. 3D printing has the ability to solve this problem as all you need for a 3D printer to work is a digitally acquired file and some filament. 3D printers can grant each manufacturer full control over their production line and allow them to waste less material while doing so.
3D printing also has other advantages over other, more traditional manufacturing methods when it comes to decreasing carbon emission rates. These are all results of the manufacturing conditions that are inherent to additive manufacturing.

Little Material Waste
Let’s compare 3D printing to another manufacturing method like CNC. The CNC method requires a blank that is later cut by machines to make the end products. The cut material from the raw blank material will be completely wasted.
For a comprehensive comparison between 3D printing and CNC: 3D Printing vs CNC: Which One is the Better Option for You?
In 3D printing, every product is made from scratch with the exact amount of material that the end product needs. There are some exceptions, like prints that require support but other than that, the material you use is usually what you get.
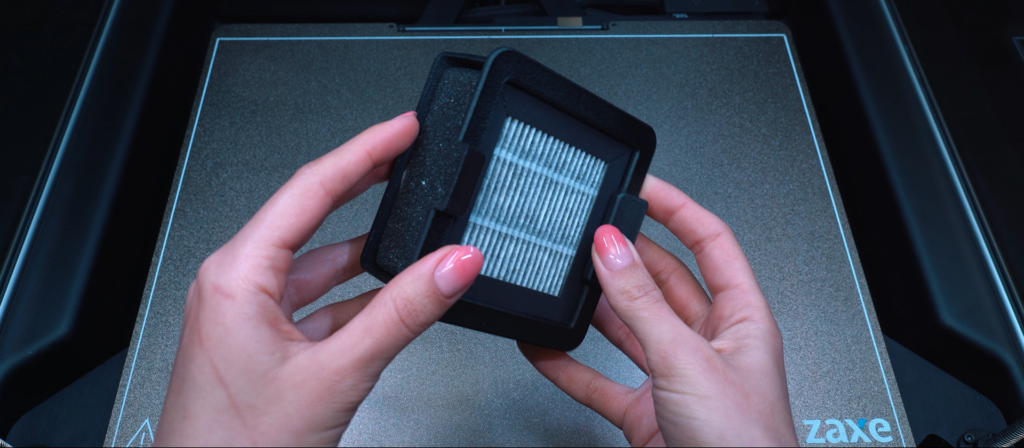

Filtered Systems
The big factory with black smoke coming out of its chimney is a cliche frame we are all familiar with. While it is a little dramatized in pop culture, it is still not that far from the truth. Depending on the company, little effort goes to filtering the carbon dioxide that comes from those factories, and even when they do use filters, they do so in inefficient ways by taking advantage of the legal loopholes of the country they are in.
Depending on the filament being used, 3D printers might not even need any sort of filtration system to not harm the environment. Even in the cases where you need to filter your individual 3D printer, it is a much easier and cheaper process. Both of our current models, Zaxe Z3 and X3 for example have fully enclosed systems that use HEPA filters to filter out anything toxic.

Source: To buy a 3D Printer
Environmentally Friendly Filaments
Most manufacturing methods won’t even come close to the number of options additive manufacturing offers when it comes to the materials that can be used. There are countless filament options available for both professionals and enthusiasts.
Manufacturers that are concerned about the environment and want to reduce the carbon emissions rates of their company can easily switch from a non-eco-friendly material to a fully recyclable one.
What are the Most Environmentally Friendly Filaments?
The filament you use will play a big part in how environmentally friendly your production methods are. Biodegradable filaments that are made from sustainable raw materials are usually the best while plastics that are derived from petrol are considered to be more harmful. Here are a couple of filament recommendations for a more eco-friendly business.

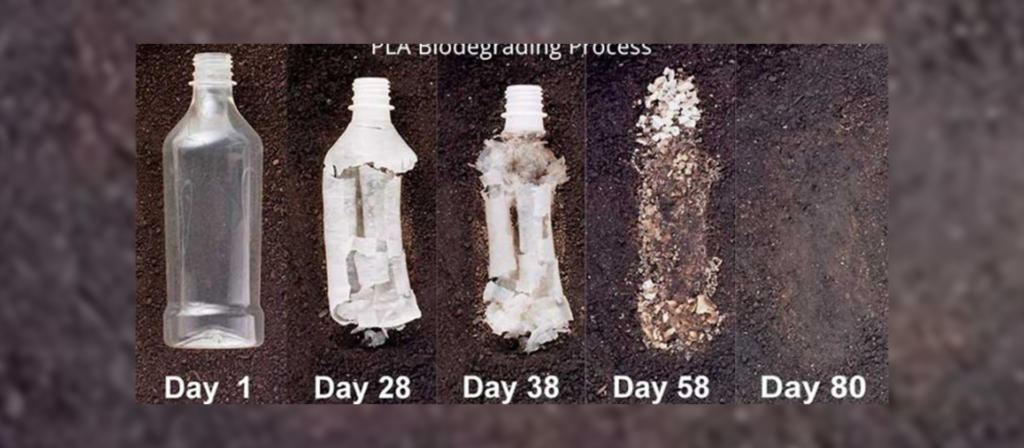
PLA
Plastic has a reputation for being harmful to the environment, but PLA is fighting that negative reputation. This will be the most widely available filament that can be considered eco-friendly. PLA is biodegradable under certain conditions and is recyclable so it would be a good start for a more eco-friendly approach to manufacturing.
Source: MaterialDistrict
Recycled Nylon
Keep an eye out for filaments that are made from recycled materials if you want to be more mindful of the way you use your 3D printer. There are companies out there that recycle fishing nets that were left by fishers at seas and turn them into filaments.

Source: 3DPrintingIndustry
rPETG
The same thing goes with rPETG, which means recycled PETG. Medical and food packing creates an unbelievable amount of wasted plastic every year so some companies recycle these wasted materials into filaments to reduce the amount of plastic wasted on 3D printing.
CNC Kitchen has a great video on recycling filament on his YouTube channel: Recycle your failed 3D prints! Make new filament at home.
Future of Eco-Friendly 3D Printing
One of the best things about 3D printing is that it hasn’t even reached a fraction of its full potential. Both FDM and SLA are technologies that are expected to evolve immensely in the future and with developments that make the technology more effective and productive, 3D printing companies will find new ways to make 3D printers that waste less energy and better recycled filaments.
The traditional methods that we have talked about are only about producing more products faster and cheaper. There is not as much of a push for innovation as there is in 3D printing because most of these methods only care about the short-term profits they are planning to make. But as it stands now, 3D printing has the potential to be the most environmentally friendly production method in the future.
