
3D Printing vs CNC: Which One is the Better Option for You?
Thanks to the developments in manufacturing technology, we now have access to more methods of production than we ever did before. While old school technologies like injection molding and pressing are reliable to this very day, they do not offer the flexibility that the newer, computer-aided methods do.
If you are looking for one of those flexible and accurate ways of manufacturing, chances are you have come across the debate “3D printing vs CNC”.
Being arguably two of the most prevalent manufacturing methods, 3D printing and CNC have a couple of similarities that attract the same type of audience and you might be one of those people who are not sure which one is better. But before you invest in one of these technologies, you should have a better idea of what they are, how they work, and what their weaknesses and strengths are so you can make the best choice for your business.
What are 3D Printing and CNC?
To understand 3D printing and CNC, first, you must have a grasp on the fundamentals of both manufacturing methods. Most people already have a superficial understanding of what 3D printing is. The name is pretty self-explanatory and the freedom it offers has already garnered the attention of the masses in recent years, but CNC is a more niche subject familiar mostly to manufacturers.
3D printing, also commonly referred to as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating a 3D object from scratch using different materials. There are two dominant technologies in 3D printing. FDM printers have a print head that extruded material from a spool of filament layer by layer to turn a digital file into a 3D object while SLA printers utilize a photochemical process that turns liquid resin into a solid object using light.
CNC on the other hand stands for computer numerical control and is a fundamentally different method of manufacturing that uses computer controller tools, called cutters, to carve raw material into the desired shape. It is similar to 3D printing in the sense that they both use a digital design to automatically make a product, but CNC requires a solid chunk of material that is referred to as a blank.
To summarize it simply, 3D printing turns material into things while CNC cuts the material into things.
Comparisons
Now that the basics are out of the way, we can compare the two methods on different aspects that are important for manufacturers. These will be the determining factor in which manufacturing methods you are going to choose.
Flexibility
Depending on the industry you are in, the expectation of your customers can be very dynamic. So, the agility of your manufacturing methods will play a huge role in the satisfaction of your customers. With additive manufacturing, you will have the ability to change designs as fast as you can use a CAD tool. After the design is changed the printing process will stay pretty much the same.
With CNC, the setup process will be much longer. The adjustment of the cutters and the testing period to make sure that the setup is correct will take longer. The geometric complexity of the end product will also depend on the capability of your machine and cutter and will be inferior to the complexity you can achieve with a 3D printer.

Cost
There will be different factors at play when you are trying to determine which manufacturing method will be more cost-efficient. If your business involves rapid prototyping or the products that you manufacture change frequently, 3D printing will be more cost-efficient for you because the setup process of additive manufacturing is much faster.
If you are planning to manufacture the same product for a long time without ever making changes in the design of the product then CNC will be more profitable for you in the long run. Once the initial setup process of the cutters is over, CNC is able to manufacture the same exact model faster than 3D printing.
If you want to spend less and print more: 3D Printing on a Budget: How to Cut Costs While Printing
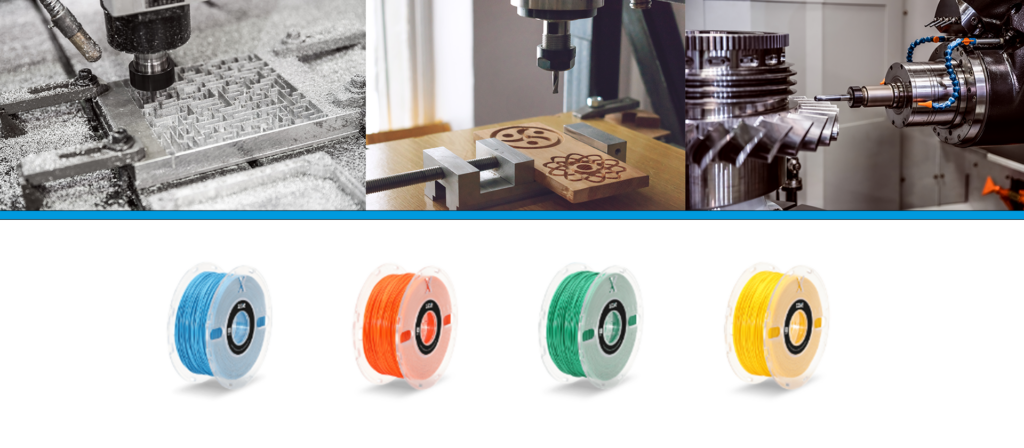

Materials
While there are countless filament options for 3D printing and the number of materials that are compatible with 3D printers in the market is increasing every year, you will still be limited to the capabilities of your device. Each 3D printer on the market will be compatible with different types of filaments like ABS, PLA or PET-CF and you will have to choose one of those filaments.
CNC has more freedom in this aspect. Subtractive manufacturing in general can be considered material agnostic as any material that you can cut through will be fit for production. In CNC, if the material you want to use has enough structural integrity to keep its shape during the cutting process, that usually means you can use the material.
For more information on materials used in 3D printing: Filaments 101
Speed
It is hard to compare the speed of 3D printing and CNC to each other because they excel at different things. 3D printing surpasses pretty much any other manufacturing method at producing the first product of the batch. If you already have an .stl file of the product, all you have to do is to drop it on your slicer and you are good to go.
As we have mentioned before, the initial setup process of CNC is much longer than 3D printing. You will have the adjust the cutters and choose the right tools to even start production. But once the setup is over and you want to move to mass production, CNC will catch up with 3D printing and surpass it when it comes to how many units you can produce in a given time period.
Sustainability
There is a common misconception that all plastic is bad for the environment. It is true that some plastics are not biodegradable and the plastics that are derived from petrol have less than stellar effects on the environment but 3D printing comes with the option to use environmentally stable filaments like PLA. PLA is one of the most popular filament types that are used in 3D printing today and it is derived from corn starch and can be completely biodegraded in the right condition. Not only that but there are companies out there that make filaments 100% from recycled materials like rubber tires and nylon fishnets.
CNC’s shortcoming is the material you are going to waste. The blank will be much bigger than the end product and the cutters will have to carve a lot of material to manufacture the product. The cut material will inevitably go to waste which means the CNC method uses more material to make the same product than 3D printing.
If you are interested in 3D printing and sustainability: Is 3D Printing Environmentally Friendly?
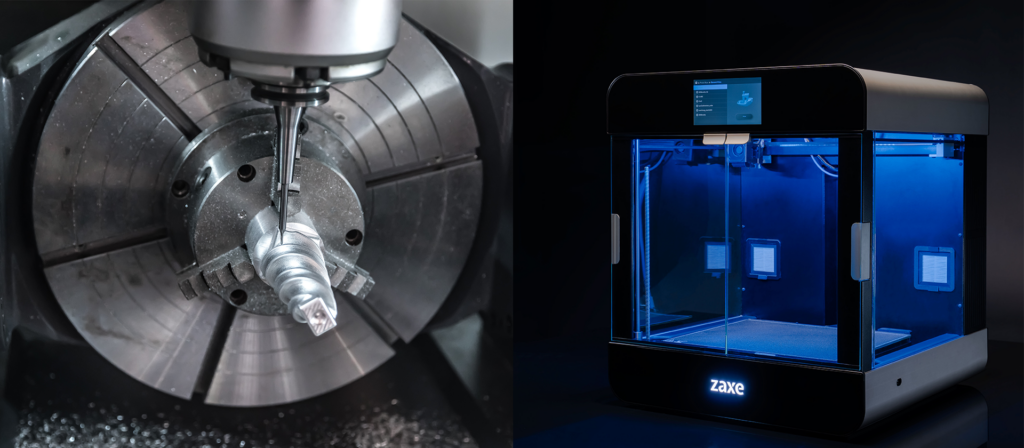
Which is the Better Fit for You?
CNC will be better at mass production and has the capability of working with a wider array of materials. The maximum dimension of a product that is manufactured with CNC will also be bigger. But the setup times, being limited to the ability of the cutters and the amount of material you waste will hold CNC back.
3D printing will be more agile, it will be able to manufacture products with more complex geometries and is able to help with rapid prototyping. But it will be slower if you want to make thousands of the same product.
Based on the information we just gave you, you probably already have a solid idea of which one is the right choice for you. If not, you will have to weigh the pros and cons of both methods and determine the right method yourself. While we can give you all the information you need, we can’t make the decision for you.
